Traditional vs. Digital Advertising: A Complete Comparison

Senior WebCoder
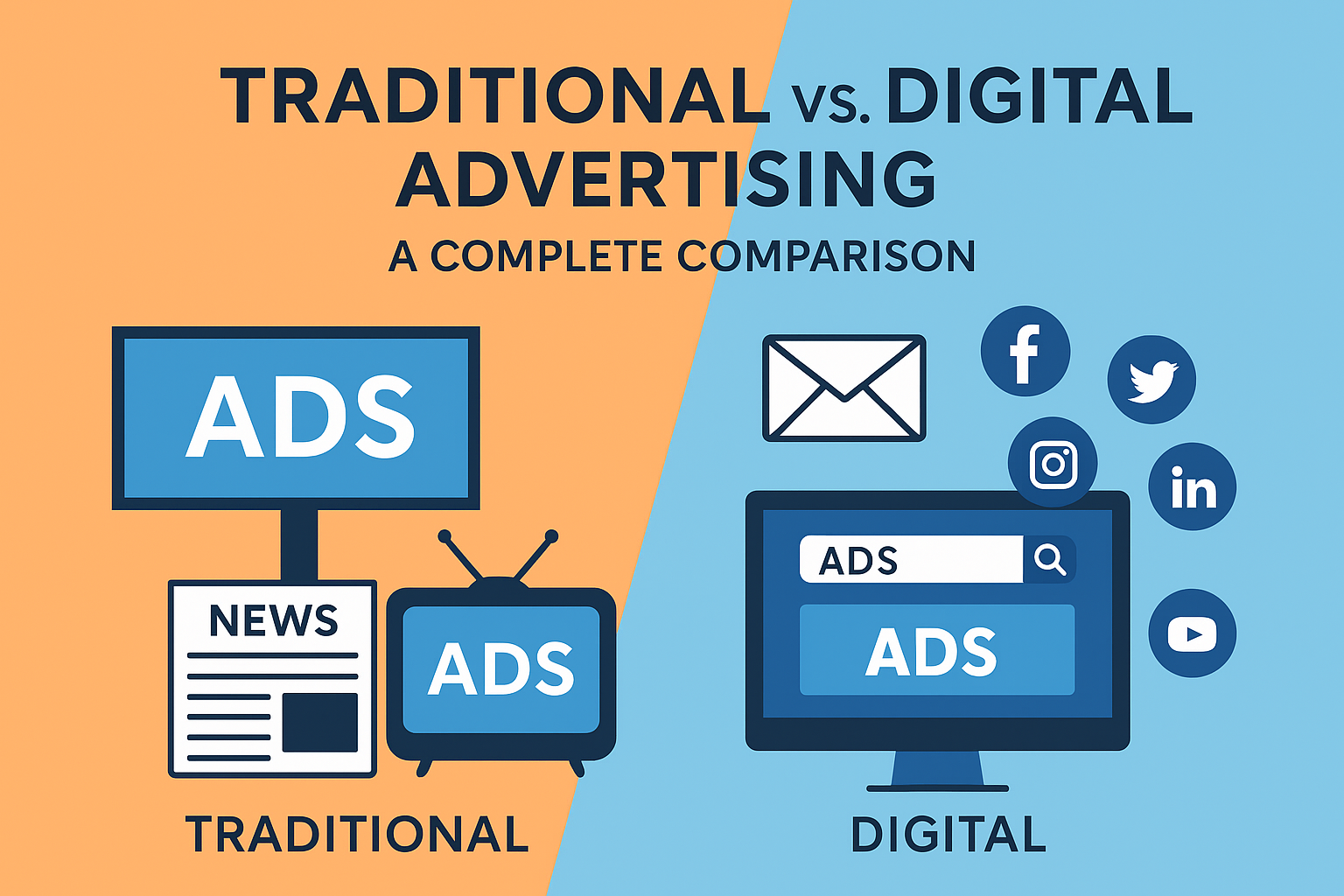
Marketing is the bridge between a business and its audience. Over the years, the way brands communicate with consumers has evolved dramatically. While traditional advertising has been the backbone of marketing for decades, digital advertising has revolutionized how businesses reach, engage, and convert their audience. Understanding the differences, strengths, and limitations of both is crucial for any business seeking growth.
What is Traditional Marketing?
Traditional marketing refers to offline marketing methods that existed before the rise of the internet. It focuses on physical channels to reach a wide audience, such as newspapers, magazines, TV, radio, billboards, and direct mail campaigns.
Traditional marketing relies heavily on mass communication, targeting audiences based on location, demographics, or general interest rather than behavior or online activity.

Why Traditional Marketing?
Despite the rise of digital channels, traditional marketing remains effective for several reasons:
- Local Reach: Attracts nearby customers through billboards, flyers, or local newspapers.
- Brand Credibility: TV commercials and print ads are often perceived as more trustworthy.
- Tangible Impact: Physical materials like brochures, catalogs, or posters leave a lasting impression.
- Broad Exposure: Reaches audiences who may not use digital platforms, such as older demographics.
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing uses online platforms and digital technologies to promote products or services. This includes social media, search engines, email, websites, apps, and more.
Unlike traditional marketing, digital marketing allows for highly targeted campaigns based on user behavior, preferences, and engagement. It also provides real-time performance tracking and measurable results.

Why Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing has become essential for modern businesses due to its flexibility and efficiency:
- Targeted Marketing: Campaigns can focus on specific audiences based on demographics, behavior, or interests.
- Cost-Effective: Paid digital campaigns are often more affordable than TV or print ads.
- Measurable Results: Analytics tools track clicks, impressions, conversions, and ROI.
- Global Reach: Digital campaigns can reach international audiences instantly.
- Engagement: Allows direct interaction with customers through comments, likes, shares, and messages.
Types of Traditional Marketing
Print Media
- Includes: newspapers, magazines, brochures, flyers, posters
- Example: A clothing brand placing an ad in a fashion magazine.
- Pros: Tangible, memorable, builds brand credibility
- Cons: Limited targeting, expensive for premium publications

Broadcast Media
- Includes: TV and radio ads
- Example: A soft drink brand airing commercials during prime time.
- Pros: Mass exposure, strong audio-visual impact
- Cons: High production cost, difficult ROI tracking
Outdoor Advertising
- Includes: Billboards, posters, transit ads, signage
- Example: A tech company advertising a new smartphone on a highway billboard.
- Pros: Constant visibility, repeated exposure
- Cons: Hard to measure, expensive for prime locations

Direct Mail
- Includes: Catalogs, postcards, flyers
- Example: A furniture store mailing seasonal catalogs.
- Pros: Targeted, tangible
- Cons: Can be seen as junk mail, costly for large distribution
Events and Sponsorships
- Includes: Trade shows, exhibitions, local event sponsorships
- Example: A car brand sponsoring a sports event.
- Pros: Personal connections, direct engagement
- Cons: High organizational cost, limited reach
Types of Digital Marketing
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Includes: Optimizing website content for search engines
- Example: An e-commerce store ranking for “best running shoes.”
- Pros: Sustainable traffic, builds authority
- Cons: Time-consuming, requires continuous updates

Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
- Includes: Paid search campaigns (Google Ads)
- Example: Paying for an ad when someone searches “affordable web hosting.”
- Pros: Immediate visibility, highly targeted
- Cons: Requires budget and optimization, competitive
Social Media Marketing
- Platforms: Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok
- Example: A makeup brand running Instagram ads for women aged 18–35.
- Pros: Highly targeted, interactive engagement
- Cons: Organic reach can be limited, requires constant content creation

Content Marketing
- Includes: Blogs, videos, infographics, e-books
- Example: A travel company publishing “Top 10 Weekend Getaways in India.”
- Pros: Builds authority, supports SEO
- Cons: Long-term results, time-intensive
Email Marketing
- Includes: Promotional or informational emails
- Example: Online stores sending discount offers to newsletter subscribers.
- Pros: Personalized, measurable
- Cons: Can be perceived as spam, requires quality email lists
Influencer Marketing
- Includes: Partnering with online personalities
- Example: Fitness brands collaborating with YouTube coaches.
- Pros: Builds trust, reaches niche audiences
- Cons: Cost varies, ROI can be hard to measure
Affiliate Marketing
- Includes: Paying commissions to partners
- Example: Software companies paying bloggers for referral sales.
- Pros: Performance-based, expands reach
- Cons: Depends on affiliates’ efforts, requires tracking
Display Advertising
- Includes: Banner ads, pop-ups, retargeting
- Example: Retargeting shoes to users who visited an e-commerce site.
- Pros: Increases brand awareness, re-engages potential customers
- Cons: Can be ignored or blocked by ad blockers
Pros and Cons Comparison
Traditional Marketing
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Credibility | High brand credibility and trust | Hard to measure ROI accurately |
| Audience | Effective for local audience targeting | Limited targeting and segmentation |
| Experience | Tangible and memorable | Slower feedback and adjustment |
| Accessibility | Reaches audiences without internet access | Expensive, especially for TV or radio |
Digital Marketing
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Targeting | Highly targeted and personalized campaigns | Ads can be ignored due to ad blockers |
| Cost | Cost-effective and scalable | High competition for attention |
| Performance | Real-time tracking and analytics | Requires technical skills |
| Reach | Global reach | Negative feedback can spread quickly |
| Engagement | Interactive engagement | — |
Digital Marketing vs. Traditional Marketing: Key Differences
| Feature | Traditional Marketing | Digital Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Channel | Offline (TV, print, billboards) | Online (social, search engines, email) |
| Cost | Higher for large campaigns | Lower, flexible budgets |
| Audience Targeting | Broad, demographic-based | Highly specific, behavior-based |
| Measurability | Hard to track ROI | Easy to measure & optimize |
| Engagement | Passive | Interactive, engaging |
| Speed | Slower to implement & adjust | Quick to launch & modify |
Which Type of Marketing Should You Use?
The choice depends on your business goals, audience, and budget:
- Traditional Marketing: Ideal for local awareness, older audiences, and building credibility.
- Digital Marketing: Best for measurable results, engaging younger or tech-savvy audiences, and scaling globally.
- Hybrid Approach: Combining both channels leverages the strengths of each, offering broad reach with precise targeting and measurable results.
Conclusion
Both traditional and digital marketing have their unique advantages. Businesses that understand these channels can design effective campaigns that maximize brand visibility, audience engagement, and return on investment.
